Type 2 Brugada Syndrome Ecg

Risk stratification for accurate identification and treatment of individuals at high risk of scd.
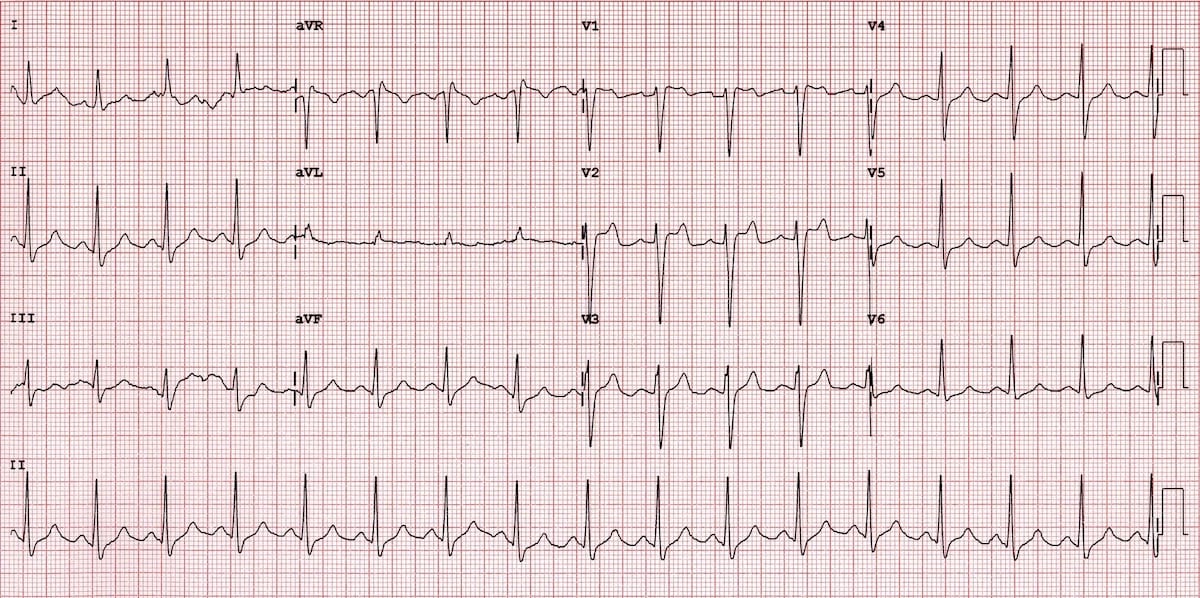
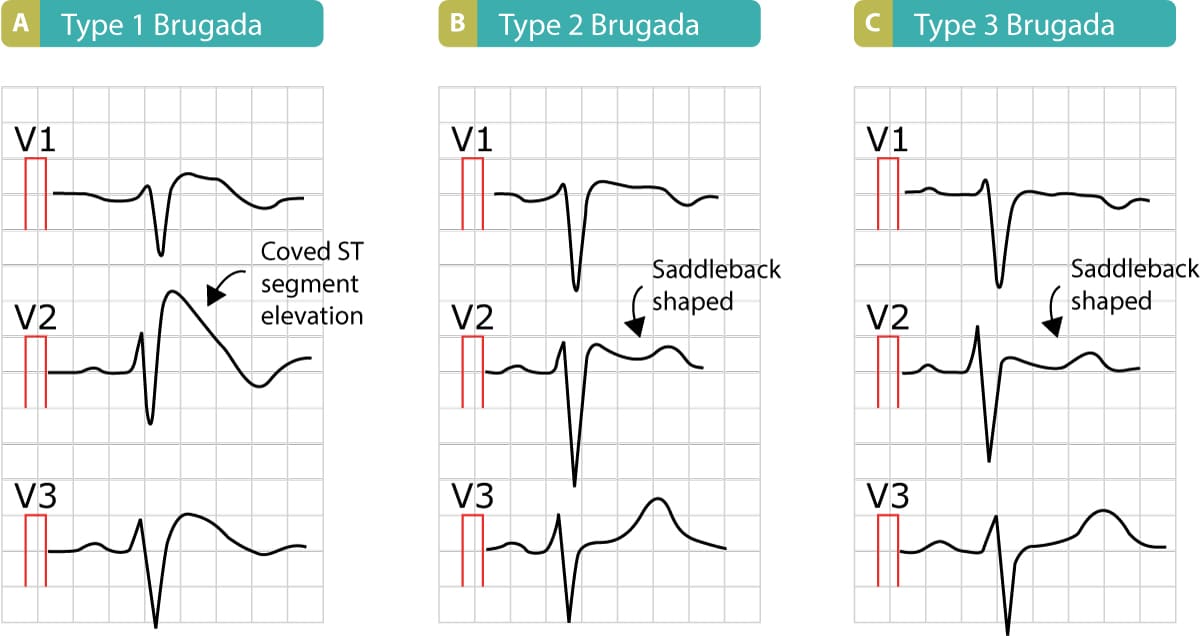
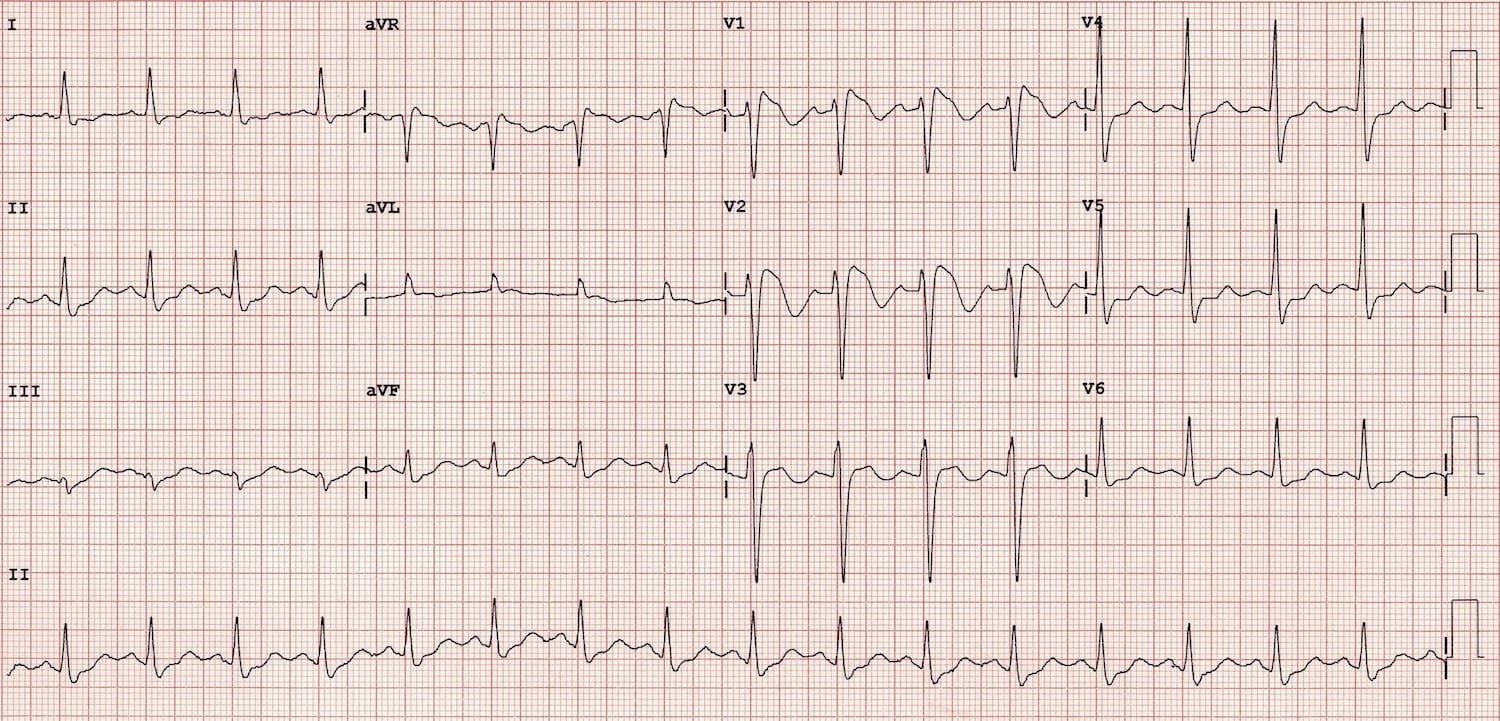
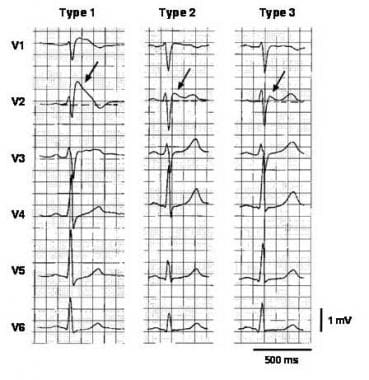
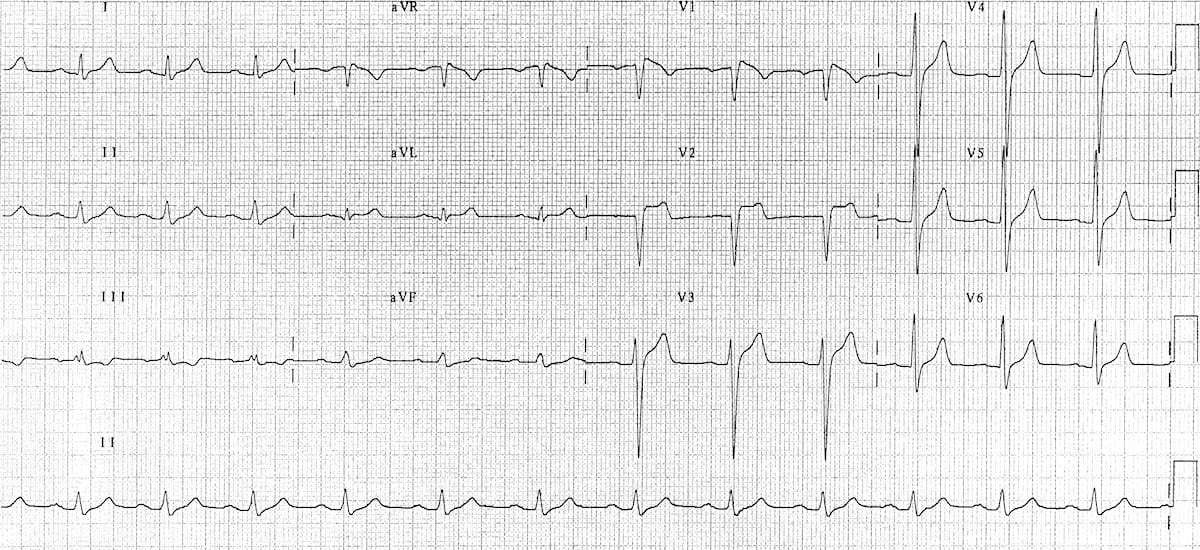
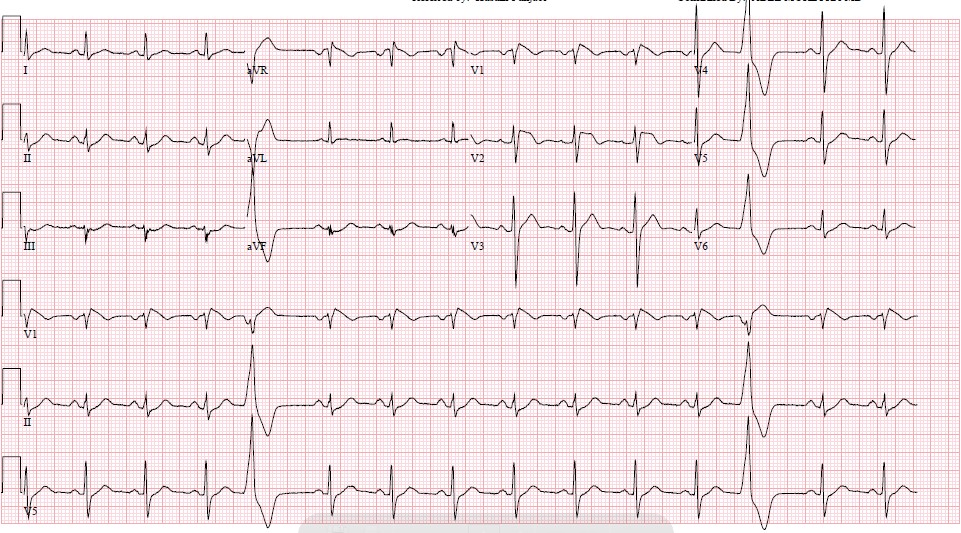
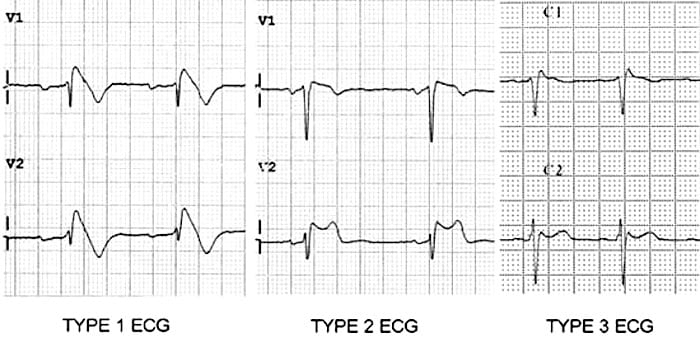
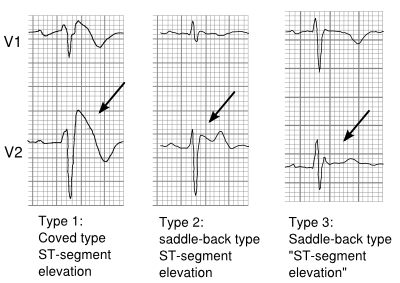
Type 2 brugada syndrome ecg. Diagnosis ecg ekg brugada syndrome comparison types typeiii. A type iii ecg is rather common and is considered a normal variant but also the type ii is a normal variant albeit suggestive of brugada syndrome. Electrocardiograms of brugada patients can change over time from type i to type ii and or normal ecgs and back. Type 2 has a saddle back pattern with at least 2 mm j point elevation and at least 1 mm st elevation with a positive or biphasic t wave.
The mean age of sudden death is 41 with the age at diagnosis ranging from 2 days to 84 years. Brugada syndrome is a disorder characterized by sudden death associated with one of several electrocardiographic ecg patterns characterized by incomplete right bundle branch block and st. Figure 2 shows a proposed diagnostic algorithm. Saddleback shaped st segment elevation with j point elevated 2 mm in leads v1 and or v2.
Is this type 2 brugada syndrome ecg pattern. Brugada syndrome is an abnormal ecg right bundle branch block pattern with coved st elevation over the right precordial leads of v1 v3 which leads to ventricular fibrillation vf and sudden cardiac death scd in patients with structurally normal hearts. R wave at least 2 mm in v1 or v2 2. First described in 1992 by the brugada brothers the disease has since had an exponential rise in the numbers of cases reported.
Three forms of the brugada ecg pattern have been described type 1 has a coved type st elevation with at least 2 mm 0 2 mv j point elevation and a gradually descending st segment followed by a negative t wave. If a type 1 ecg is observed in the absence of any clinical criteria this should be referred to as idiopathic brugada ecg pattern and not as bs4. The difference between type 2 and type 3 is that the st segment elevation in type 2 is elevated 2 millimeters it is lower in type 3 brugada syndrome. Note that the electrodes to lead v1 and v2 may be placed in the second third or fourth intercostal space in the pursuit of these ecg changes.
They use terminology of concave downward 4. Type 2 brugada syndrome. The peak at the high takeoff does not. The terminal portion of the st segment is elevated 1 mm.
But no distinct r wave because the st segment takes off at an angle from the peak 3. Refer to figure 1. The st segment is convex upward coved.